
Pain Around Ribs and Back: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Introduction
Rib and back pain is a common problem that affects many people. It can feel like a sharp, stabbing pain or a dull ache, making it uncomfortable to move, breathe, or sit for long periods. This kind of pain can be caused by simple things like a pulled muscle, or it might be a sign of something more serious, like issues with your lungs, kidneys, or even your heart.
The pain around your ribs and back can happen for different reasons. It might be due to an injury, like a rib fracture, or conditions like muscle strains from lifting something too heavy. In some cases, it can be caused by medical problems, such as kidney stones, gallbladder inflammation, or lung infections. It’s important to understand the symptoms and know when to seek medical attention, especially if the pain doesn’t go away or gets worse.
This article will explain the common causes of rib and back pain, the symptoms to watch out for, and when it’s time to visit a doctor. By understanding what might be causing your discomfort, you can take steps to feel better and avoid more serious problems.
Common Causes of Pain Around Ribs and Back
Pain around your ribs and back can come from different sources, ranging from minor muscle strains to more serious internal organ issues. Understanding the cause is important for proper treatment and to prevent the problem from getting worse. Below are the main categories of causes for rib and back pain.
Musculoskeletal Causes
Musculoskeletal problems are one of the most common reasons for rib and back pain. This type of pain is often related to issues with the muscles, bones, or ligaments around the ribs and back.
- Intercostal muscle strain: The intercostal muscles are the muscles located between your ribs, and they help you breathe and move your upper body. Straining these muscles from activities like heavy lifting, sudden twisting, or even excessive coughing can cause sharp pain in the ribs and back.
- Poor posture: Sitting for long periods with poor posture can lead to back and rib muscle strain. When you slouch, the muscles in your back and rib area become overstretched, leading to discomfort and pain.
- Sprains: A sprain occurs when the ligaments around the ribs or spine are overstretched or torn. This can happen from an awkward movement or lifting something too heavy, causing pain that may be felt in the back and around the ribs.
Rib Injuries and Fractures
Rib injuries are another common cause of pain in the ribs and back. These injuries can range from mild bruises to more serious rib fractures.
- Bruised ribs: A direct blow to the chest, such as from a fall or accident, can cause bruised ribs. This can result in tenderness and pain that is felt when moving or pressing on the ribs.
- Broken ribs: A more serious injury, rib fractures, can cause sharp pain when you breathe, cough, or move. A broken rib usually heals on its own, but the pain can last several weeks and can be felt in the back and chest.
- Rib cage trauma: Any severe impact to the chest area, like in sports or car accidents, can lead to trauma that affects the ribs and nearby muscles. This type of injury can make breathing and movement difficult due to the pain.
Medical Conditions Affecting Ribs and Back

Some internal medical conditions can also cause pain in the ribs and back. These conditions often affect nearby organs and can radiate pain to the ribs and back area.
- Kidney stones: When hard deposits form in your kidneys, they can cause severe pain that starts in the back and can spread to the ribs. This pain is often described as sharp and comes in waves.
- Gallbladder issues: Inflammation or stones in the gallbladder can cause pain under the ribs on the right side, which can radiate to the back. This pain is usually accompanied by nausea and can worsen after eating fatty foods.
- Pleurisy: Pleurisy occurs when the lining around the lungs becomes inflamed. This can cause sharp pain in the chest and back, especially when breathing deeply or coughing.
- Liver inflammation: Conditions such as hepatitis or liver inflammation can cause discomfort under the ribs on the right side. This pain can also radiate to the back and is often associated with other symptoms like jaundice (yellowing of the skin).
- Gastrointestinal disorders: Problems like gas buildup, indigestion, or even acid reflux can cause pain in the upper abdomen that sometimes spreads to the ribs and back, causing discomfort in both areas.
Symptoms of Pain Around Ribs and Back
The symptoms of rib and back pain can vary depending on the cause. The pain might feel sharp and sudden, or it could be a dull, constant ache. These symptoms can make simple activities like breathing, moving, or sitting difficult. Recognizing the type and severity of the pain can help determine whether it’s a minor issue or something that requires medical attention.
Common Symptoms
Here are some common symptoms of rib pain that you might experience:
- Sharp pain: You may feel a sudden, intense pain in your ribs or back, especially when you move, cough, or take deep breaths. This kind of pain is often associated with muscle strain or rib injuries.
- Pain when breathing: If you notice discomfort or sharp pain when taking a deep breath, it could be due to inflammation in the muscles between the ribs (intercostal muscles) or an issue with the lungs.
- Rib tenderness: Pressing on the ribs or the area around them might feel tender or sore, especially if you’ve bruised or fractured a rib.
- Back stiffness: If your back feels stiff, particularly after sitting or sleeping for long periods, this could indicate muscle strain or poor posture affecting your ribs and back.
- Radiating pain: Sometimes, pain that starts in the ribs can spread (or “radiate”) to your back, shoulders, or chest, making it difficult to pinpoint the exact source.
When Pain Could Indicate a Serious Condition
While many types of rib and back pain can be managed at home, some serious symptoms of rib and back pain require immediate medical attention. These could signal more critical conditions like heart problems, lung issues, or internal organ complications.
- Heart attack symptoms: Pain around your ribs, especially if it radiates to your left arm, jaw, or back, could be a warning sign of a heart attack. If this pain is accompanied by shortness of breath, sweating, or nausea, seek emergency medical care immediately.
- Referred pain: Sometimes, pain in your ribs or back might actually come from another area of the body, like your kidneys or gallbladder. This type of referred pain can signal issues like kidney stones, gallbladder inflammation, or even lung infections.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing or pain that gets worse when you breathe deeply might be a sign of pleurisy (inflammation of the lung lining) or other lung issues.
- Jaundice: If your rib pain is accompanied by yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice), this could indicate liver or gallbladder problems.
- Severe and persistent coughing that leads to rib or back pain may signal lung issues such as pneumonia or bronchitis. Continuous coughing strains the muscles around the ribs, causing discomfort.
Diagnosing Rib and Back Pain
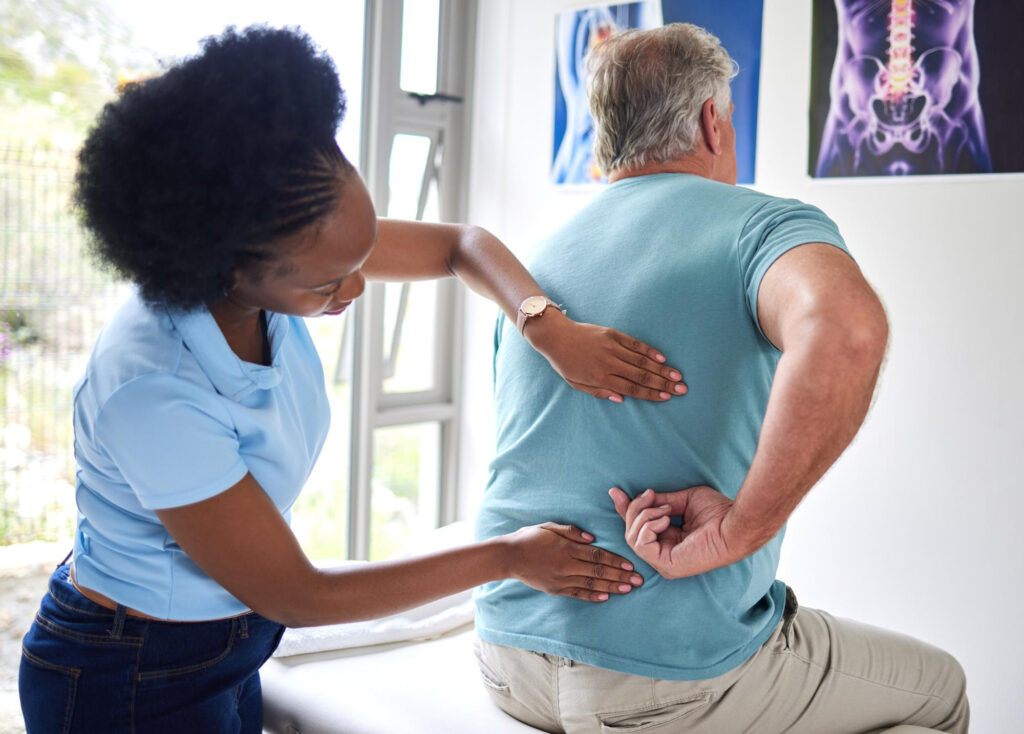
Diagnosing the cause of rib and back pain can be tricky because so many different factors can contribute to it. A proper diagnosis usually starts with a physical exam and, if needed, further imaging tests or other diagnostic procedures to pinpoint the problem. This process helps doctors figure out whether your pain is due to a muscle strain, an injury, or an underlying medical condition.
Physical Examinations
During a physical exam for rib pain, your doctor will ask you questions to understand your symptoms better. They’ll want to know when the pain started, what makes it worse or better, and if you have other issues like trouble breathing.
Next, they will carefully check the area by feeling for tenderness, stiffness, or signs of swelling. This helps them figure out if you have a muscle strain, a rib injury, or something else causing the pain. The goal is to identify what’s causing the pain so they can suggest the right treatment.
- Range of motion tests: Your doctor might ask you to move your arms, twist your torso, or take deep breaths to see how your ribs and back respond. This helps them assess if the pain worsens with movement and which muscles or joints might be involved.
- Palpation and tenderness check: The doctor will gently press on your ribs, back, and chest to identify areas of tenderness or swelling. This can help them locate the exact spot of pain and check for any abnormalities like fractures or muscle strain.
Diagnostic Imaging and Other Tests
If the physical exam doesn’t clearly show what’s causing the pain, your doctor may suggest imaging tests like X-rays or an MRI. These tests help get a better view of your bones, muscles, and organs around your ribs and back to find the problem more accurately.
- X-rays: X-rays are often the first imaging test used to check for bone fractures or abnormalities in the ribs or spine. They can help identify problems like rib fractures or other injuries affecting the bones.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): An MRI provides a more detailed view of the soft tissues, like muscles, tendons, and ligaments. It’s useful if your doctor suspects a muscle tear or other soft tissue damage.
- CT scan: A CT scan offers a more detailed look at both the bones and soft tissues. It’s often used if there’s a need to check for underlying medical conditions like kidney stones or lung issues that might be causing the pain.
- Nerve conduction studies: If the pain seems to be related to nerve damage, nerve tests can check how well your nerves are functioning. This is especially useful if you’re experiencing radiating pain or numbness.
- Blood tests: If your doctor thinks you may have an infection or an issue with your internal organs, they might suggest a blood test. This test can show signs of inflammation or infection in the body. For example, it can help detect problems like gallbladder issues or pleurisy, which is inflammation of the lining around the lungs.
By using a mix of these tests, including blood tests and imaging, your doctor can figure out the exact cause of your rib and back pain. This helps them choose the best treatment for your specific problem.
Treatment Options for Rib and Back Pain
When dealing with rib and back pain, it’s important to find the right treatment based on the cause of the pain. Treatments can range from simple at-home remedies to more advanced medical procedures. Your treatment plan will depend on how bad your pain is and whether it’s caused by a muscle injury, a bone issue like a fractured rib, or an underlying medical condition. The doctor will recommend treatments based on the root cause and severity of the pain.
At-Home Remedies and Pain Management
For mild to moderate rib and back pain, there are several home remedies you can try to manage your discomfort and promote healing.
- Rest: One of the best things you can do is give your body time to heal. Avoid activities that put stress on your ribs or back, like heavy lifting or twisting movements. But don’t completely stop moving; gentle activity can help maintain flexibility.
- Ice therapy: Applying an ice pack to the painful area for 15-20 minutes at a time can reduce swelling and numb pain. This is especially helpful for muscle strains or rib injuries like bruises or fractures.
- Anti-inflammatory medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen can help ease pain and reduce swelling caused by inflammation. These medications are often used to manage mild to moderate discomfort. These are commonly used for muscle pain or mild injuries, and they can provide relief while your body heals.
- Gentle stretching: Light, gentle stretches can help prevent stiffness in your back and improve flexibility. Be careful not to overdo it—move slowly and stop if you feel any pain.
These home remedies can often provide relief, but if your pain doesn’t improve after a few days or if it gets worse, it’s important to see a doctor.
Medical Treatments and Procedures
If your rib and back pain lasts a long time or becomes more severe, you may need medical treatments to help with the pain and target the underlying cause.
- Corticosteroid injections: If your pain is caused by swelling near your ribs or spine, your doctor may suggest a corticosteroid injection. This shot helps reduce inflammation and gives relief, especially if regular pain medicines don’t work well enough.
- Physical therapy: If your pain is related to muscle strain or poor posture, physical therapy can help. A physical therapist will teach you exercises to improve your posture, strengthen the muscles, and increase your flexibility. This can help relieve pain and prevent it from coming back.
- Nerve blocks: If your pain is due to nerve problems, such as a pinched nerve, your doctor might use a nerve block to numb the area. This can provide longer-lasting relief and help with chronic pain.
- Surgery: Surgery is usually a last resort, but in cases of severe injuries like multiple rib fractures or a herniated disc, surgery may be necessary. It helps repair the damage and relieves pressure on the nerves.
These treatments are generally recommended when home remedies don’t provide enough relief or when there’s a more serious issue causing the pain. Your doctor will work with you to find the best option for your specific situation.
Prevention Tips for Rib and Back Pain

Preventing rib and back pain involves taking steps to keep your body strong and protected. By improving your posture, strengthening your muscles, and practicing safe habits, you can reduce the likelihood of injuries and discomfort. Let’s explore some key prevention tips.
Maintaining Good Posture and Strengthening Muscles
One of the most effective ways to prevent rib and back pain is by maintaining good posture and keeping your muscles strong. When your posture is correct, it reduces unnecessary strain on your back and ribs, helping you avoid discomfort.
- Posture tips: Make sure to sit and stand with your back straight, shoulders relaxed, and ears aligned with your shoulders. Avoid slouching, especially when sitting for long periods. If you work at a desk, adjust your chair and screen height to encourage proper posture.
- Core exercises: Strengthening your core muscles, which include your abs and lower back, is essential for supporting your spine. Exercises like planks, bridges, and pelvic tilts can help build strength in these areas.
- Lumbar support: Using lumbar support when sitting for long periods can help maintain the natural curve of your lower back. A supportive chair or pillow can reduce strain on your back muscles and spine.
- Stretching: Regularly stretching your back, shoulders, and chest can prevent stiffness and improve flexibility. Simple stretches, like touching your toes or twisting your torso gently, help keep your muscles loose and balanced.
By following these posture correction and strengthening tips, you can protect your ribs and back from unnecessary strain.
Reducing Risk of Rib Injuries
Preventing rib injuries is all about being mindful of your body and taking steps to avoid accidents or overexertion.
- Protective gear: If you play contact sports, wearing protective gear, such as padded vests or chest guards, can shield your ribs from direct impacts. This is especially important in sports like football or hockey, where collisions are common.
- Avoiding contact sports: If you’re prone to rib injuries, it may be helpful to avoid high-risk activities like contact sports. Instead, consider low-impact exercises like swimming or walking, which can still help you stay fit without the risk of injury.
- Safe movement techniques: When lifting heavy objects, always use proper form to avoid straining your back and ribs. Bend your knees, keep the object close to your body, and lift with your legs instead of your back. Avoid twisting your torso while lifting or carrying heavy items.
By maintaining good posture, strengthening your muscles, and practicing safe habits, you can significantly reduce your chances of experiencing rib and back pain. These simple tips help you stay strong, active, and injury-free.
When to See a Doctor for Rib and Back Pain
While most cases of rib and back pain can be managed with home care, there are times when it’s important to seek medical attention. Pain in this area can sometimes signal a more serious condition that requires professional treatment. Knowing when to seek help can prevent complications and ensure that you get the right care in time.
Signs That Require Medical Attention
Certain signs of serious rib pain should never be ignored. If you experience any of the following symptoms, it’s important to contact a doctor or visit an emergency room immediately:
- Chest pain: If your rib pain is accompanied by chest pain, especially if it spreads to your arms, neck, or jaw, it could be a sign of a heart attack. This is particularly concerning if the pain is also associated with shortness of breath, sweating, or nausea.
- Difficulty breathing: If it hurts to breathe or you feel sharp pain when taking deep breaths, it could mean pleurisy (swelling of the lung lining) or a lung infection. You should see a doctor quickly to get the right care.High fever: Pain with a high fever might mean you have an infection, like pneumonia, or a problem with an organ, such as the gallbladder. This needs urgent medical help.
- Radiating pain to arms or jaw: If the pain around your ribs spreads to your arms, shoulders, or jaw, it could be a sign of a heart or lung issue. Seek emergency care if this happens, as these symptoms can indicate a serious underlying problem.
In cases of persistent symptoms, severe pain that doesn’t improve with rest, or pain that suddenly gets worse, it’s important to visit a doctor to determine the cause. Early detection and treatment can prevent more serious complications and help you get back to feeling better quickly.
Conclusion
Catching and treating rib and back pain early is important to reduce discomfort and prevent more serious problems. Whether your pain comes from a simple muscle strain or something more serious like a rib injury or a medical condition, getting treatment quickly can make a big difference in how you recover.
By understanding the signs, trying home remedies, and seeking medical help when needed, you can make sure your pain is properly diagnosed and treated. If you have severe symptoms like sharp chest pain, difficulty breathing, or pain that spreads to other areas, it’s crucial to see a doctor. Getting help early can prevent complications and help you feel better sooner.
What causes pain in the ribs and back?
Pain in the ribs and back can be caused by a variety of issues, including:
- Muscle strain: Overuse, poor posture, or heavy lifting can strain muscles between the ribs and in the back, causing pain.
- Rib injuries: Bruised or fractured ribs can lead to sharp pain that radiates to the back.
- Inflammation: Conditions like costochondritis, which is the inflammation of the cartilage between the ribs, can cause pain in both the ribs and back. This can lead to discomfort when you move or breathe deeply.
- Underlying conditions: Problems like kidney stones, gallbladder issues, and lung infections can cause pain that spreads from the internal organs to the ribs and back. These conditions often need medical treatment to prevent complications.
How to relieve back rib pain?
To relieve back rib pain, consider the following methods:
- Rest: Avoid strenuous activities that could worsen the pain.
- Ice therapy: Apply ice to the painful area to reduce inflammation.
- Anti-inflammatory medication: Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen can help reduce pain and swelling.
- Gentle stretching: Light stretching exercises can help release tension in the muscles.
- Heat therapy: Once the initial inflammation has gone down, applying heat can help relax tight muscles and reduce discomfort. Heat increases blood flow to the affected area, which can speed up healing and provide relief from muscle stiffness.
If the pain persists or worsens, it’s important to seek medical advice.
When should I be worried about rib pain?
You should be concerned about rib pain if:
- Pain spreads to your arm, jaw, or back, which could signal a heart attack.
- You experience difficulty breathing or shortness of breath, which may indicate a lung issue.
- You have a high fever with rib pain, which could signal an infection.
- The pain doesn’t improve with rest or treatment and continues to worsen over time.
In these cases, it’s best to seek medical attention promptly.
How do you know if it’s lung pain or rib pain?
To differentiate lung pain from rib pain, consider the following:
- Rib pain is often sharp and worsens with movement, breathing, or coughing. It can be tender to touch, especially if the ribs are bruised or fractured.
- Lung pain tends to be deeper and may feel more like pressure. Conditions like pleurisy (inflammation of the lung lining) can cause pain that worsens with deep breaths but isn’t tender to the touch.
- If you’re experiencing shortness of breath or coughing with pain, it might be related to the lungs.
Always consult a doctor if you’re unsure.
Can stress cause rib and back pain?
Yes, stress can cause rib and back pain. When you’re stressed, your body tends to tense up, especially in the neck, shoulders, and back. This muscle tension can extend to the ribs, causing pain or discomfort. Stress can also lead to shallow breathing, which can strain the muscles between the ribs, resulting in additional pain.
What diseases cause rib pain?
Several diseases can cause rib pain, including:
- Pleurisy: Inflammation of the lung lining that causes sharp pain, especially when breathing.
- Osteoporosis: Weakens bones, making the ribs more prone to fractures and resulting in pain.
- Costochondritis: This is the inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the breastbone (sternum). It usually causes localized pain in the chest area, especially when moving or breathing deeply.
- Kidney stones: Can cause radiating pain to the lower ribs and back.
- Gallbladder disease: Can lead to pain under the ribs on the right side, often radiating to the back.
If you suspect a medical condition is causing your rib pain, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis.











